Contribution to the knowledge on the vascular flora of aquatic and amphibious habitats along the Modrac Reservoir and adjacent marshes (Bosnia and Herzegovina)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.7251/GSF2434004NKeywords:
aquatic habitats, diversity, flora, Modrac, Mosorovac bara, Šerićka bara, wet habitatsAbstract
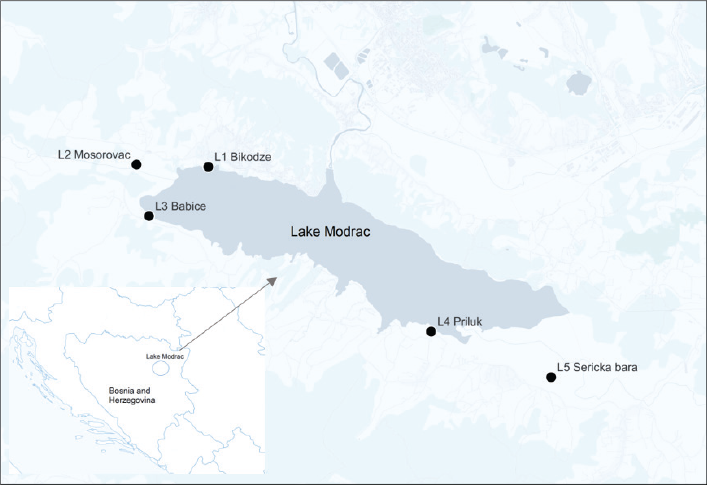
A study of the vascular flora of aquatic and amphibious habitats along the Modrac reservoir and adjacent marshes, Šerićka bara, and Mosorovac bara was conducted during the vegetation season 2018. In total, 68 plant species from 36 families were identified. The families with the highest taxa were Cyperaceae and Lamiaceae, and the most numerous genera were Carex and Mentha. The dominant plant life forms were hemicryptophytes and hydrophytes, while in chorological analysis dominated Euroasian floral elements. Generalists, the pioneers of secondary succession, and competitive species were the most common social behavior types of plants. Threatened vulnerable species Marsilea quadrifolia L., Veronica anagallis-aquatica L., the least concerned species Butomus umbellatus L., and species that are protected by Berns convention Trapa natans L. were recorded in the researched area. Invasive plant species with predominance of Echinocystis lobata (Michx.) Torr. & A. Gray, Bidens frondosus L., and Ambrosia artemisiifolia L. were common. The researched area is typical for progradational stages and intensive overgrowth of marshes with vegetation of reed and cattail, and a good representation of macrophytes Trapa natans L. and Rorippa amphibia (L.) Besser in littoral area of Modrac reservoir.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Radenko Nešković, Jasmina Kamberović

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.